OpenConnect VPN server, or ocserv, is an SSL VPN server compatible with Cisco AnyConnect.
It can easily be installed in a cheap OpenVZ Virtual Private Server (VPS) with TUN capability.
However, most online tutorials for installing OpenConnect VPN server rely on certtool to generate a self-signed certificate via OpenSSL.
Afterwards, since the self-signed certificate is not trusted by operating systems, either the VPN client must be configured to skip certificate checking, or the self-signed certificate must be imported as a trusted certificate on the VPN client machine.
Both practices are insecure.
Bypassing certificate checking would allow an attacker to impose as the VPN server.
Importing a trusted certificate does not seem wrong at first, but in case the private key is compromised, an attacker would be able to impose as any server to the client, including online shopping and bank websites, using a certificate signed by that private key.
Remember that the self-signed certificate's private key is stored on the VPS filesystem, it is much less secure than Hardware Security Modules used at real CAs to store private keys, and therefore it is a bad idea to trust such certificates in client machines.
Let's Encrypt is a free, automated, and open Certificate Authority (CA). It allows anyone to obtain a domain-verified certificate within minutes, and without paying anything. Certificates from Let's Encrypt are trusted by most modern operating systems. They are ideal for securing an OpenConnect VPN server.
This article explains how to request a proper trusted certificate from Let's Encrypt for use with ocserv, how to install OpenConnect VPN Server and use the Let's Encrypt certificate, and how to configure Cisco AnyConnect client to connect to ocserv.
These steps are verified with an OpenVZ Ubuntu 16.04 64bit VPS provided by SecureDragon.
It is required to enable TUN devices for the VPS, typically through a button in SolusVM or other control panel provided by the hosting company.
Request Let's Encrypt Certificate for OpenConnect VPN Server
Before requesting a certificate from Let's Encrypt, you must have a Virtual Private Server with an IPv4 address, and have a domain name (could be subdomain) resolved to the server so that you are able to ping the server via the domain name.
After the requirements above are met, the first step is to install certbot, a program for requesting Let's Encrypt certificates.
Executing the following commands as root installs certbot:
add-apt-repository ppa:certbot/certbot
apt-get update
apt-get install certbotThen, we can proceed to request a certificate:
certbot certonly --standalone -d ocserv.mlIt is necessary to stop any process running on TCP port 80 or 443 when running the above command, including Apache, nginx, Python or NodeJS web servers, and ocserv if you have installed it already.
See certbot site for more information on how to request a certificate without stopping your web server.
You will see the following message if the certificate is obtained successfully:
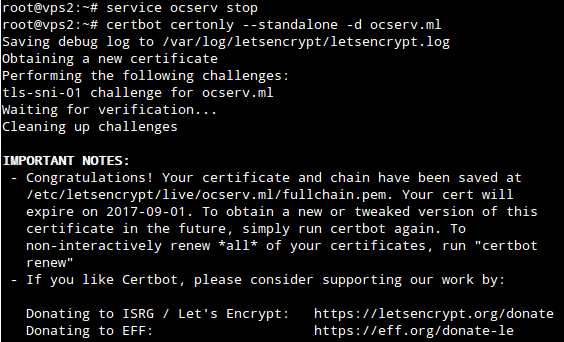
Install OpenConnect VPN Server with Let's Encrypt Certificate
To install ocserv, execute the following as root:
apt-get install ocservThen, edit /etc/ocserv/ocserv.conf:
auth = "plain[/etc/ocserv/ocpasswd]"
tcp-port = 443
udp-port = 443
run-as-user = nobody
run-as-group = daemon
socket-file = /var/run/ocserv-socket
server-cert = /etc/letsencrypt/live/ocserv.ml/fullchain.pem
server-key = /etc/letsencrypt/live/ocserv.ml/privkey.pem
max-clients = 8
max-same-clients = 0
try-mtu-discovery = true
device = vpns
ipv4-network = 192.168.91.0/28
dns = 8.8.8.8
cisco-client-compat = trueOptions server-cert and server-key should point to the certificate paths shown in certbot output.
If you want to change ocserv's listening port number to avoid conflicts with websites running on port 443:
- In
/etc/ocserv/ocserv.conf, settcp-portandudp-portto the desired port number. - In
/lib/systemd/system/ocserv.socket, setListenStreamandListenDatagramto the same port number. - Run
systemctl daemon-reloadto inform systemd that the port number has been changed.
Next step is creating usernames and passwords with ocpasswd:
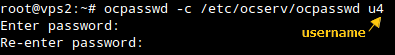
Finally, restart ocserv for the settings to take effect:
systemctl restart ocservSetup IP Routing for OpenConnect VPN Server
ocserv has been configured and is ready for connections, but if you try at this moment, Cisco AnyConnect clients can only communicate with the VPN server, but would not be able to reach the Internet.
It is necessary to setup Network Address Translation (NAT) in order to gain Internet access:
iptables -t nat -A POSTROUTING -s 192.168.91.0/28 -j SNAT --to-source 198.51.100.8
apt-get install iptables-persistentSubstitute 198.51.100.8 with the public IPv4 address of your server.
If apt-get install iptables-persistent has no effect, run dpkg-reconfigure iptables-persistent instead.
Answer YES at the following dialog, so that the iptables settings will be re-applied automatically if the server reboots:
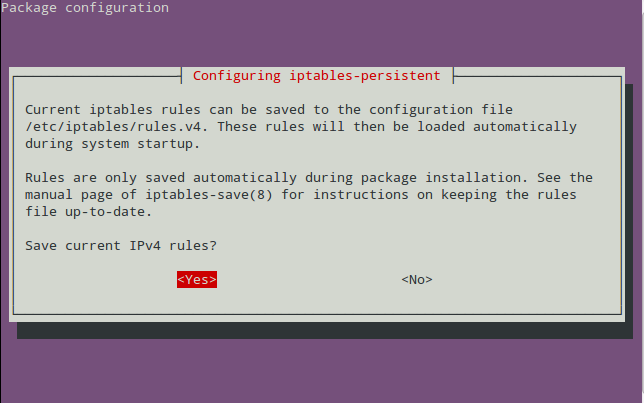
Connect to ocserv with Cisco AnyConnect Client
It is easy to connect to ocserv via Cisco AnyConnect client app.
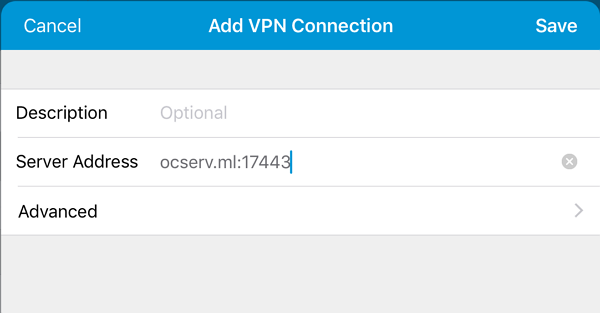
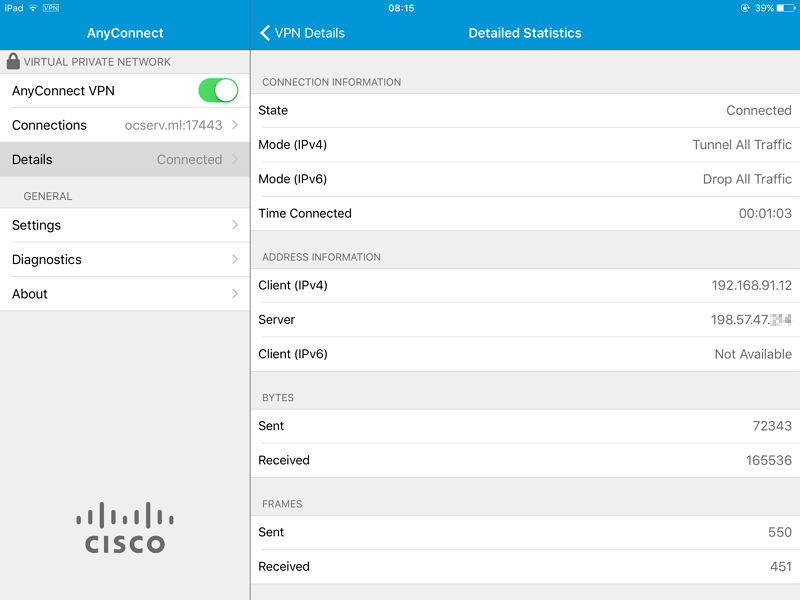
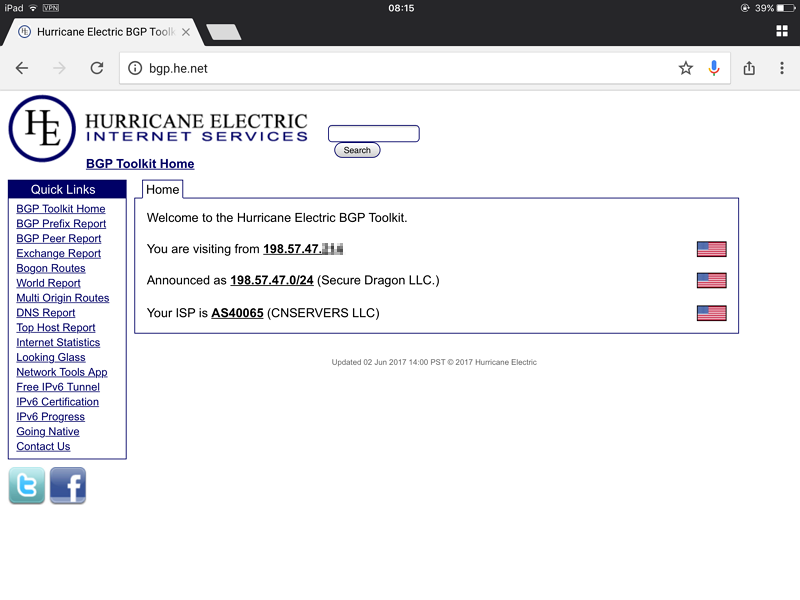
It works! There is no need to go into settings and permit untrusted servers, because the server has a trusted certificate from Let's Encrypt.